
Compressors: Types, Applications, and Future Trends
Introduction
Compressors are the backbone of many industrial and domestic applications, playing a crucial role in powering tools, machinery, and refrigeration systems. These devices are designed to increase the pressure of gases or air by reducing their volume, enabling a wide range of functionalities, from inflating tires to driving high-powered manufacturing equipment. Their significance cannot be overstated, as they contribute to efficiency, cost-effectiveness, and sustainability in various industries. These devices are specifically designed to increase the pressure of gases or air by reducing their volume, making them indispensable across a wide range of industries. Whether it is inflating a simple car tire, operating heavy-duty construction equipment, or ensuring efficient refrigeration and air compression in large-scale manufacturing plants, compressors contribute significantly to modern technology and infrastructure.
The fundamental working principle of compressors revolves around compressing air or gas into a smaller space, thereby increasing its pressure. This pressurized air or gas can then be stored and released in a controlled manner to perform various functions. For instance, in industrial settings, compressed air is utilized to drive pneumatic tools, automate machinery, and enhance energy efficiency. In the automotive industry, compressors are integral to airbrake systems, tire inflation, and even vehicle air conditioning. Similarly, in healthcare, medical air compressors are used in ventilators, oxygen concentrators, and other life-supporting equipment, demonstrating their critical role in saving lives.
One of the most significant applications of compressors lies in refrigeration and air conditioning systems. These systems rely on compressors to circulate refrigerants, enabling temperature regulation in homes, offices, and industrial cold storage units. Without compressors, the cooling process in refrigerators, freezers, and air conditioners would not be possible, affecting food preservation, pharmaceutical storage, and overall human comfort.
Compressors are also vital in the oil and gas industry, where they assist in the extraction, transportation, and processing of natural gas. Gas compressors are used in pipelines to maintain flow pressure and ensure efficient fuel transportation over long distances. Likewise, in power plants, compressors support combustion engines and turbines, optimizing energy generation for industries and households alike.
The importance of compressors extends beyond functionality, as they contribute to efficiency, cost-effectiveness, and sustainability. Many modern compressors are designed with energy-efficient technologies to minimize power consumption and reduce operational costs. With the advancement of variable-speed compressors, industries can regulate energy usage more effectively, leading to a lower environmental impact.
In conclusion, compressors are indispensable devices that support various industries, from manufacturing and healthcare to automotive and energy production. Their ability to enhance efficiency, improve productivity, and facilitate critical processes makes them an essential component of industrial and domestic operations worldwide.
Types of Compressors
Understanding the different types of compressors is essential for selecting the right one for a specific application. Broadly, compressors can be categorized into two main types: positive displacement compressors and dynamic compressors. Each type has further subcategories, each with its own unique operating principles, advantages, and applications.
Positive Displacement Compressors
Positive displacement compressors function by trapping a volume of air or gas and mechanically reducing its space, thereby increasing pressure. Within this category, the most common types include:
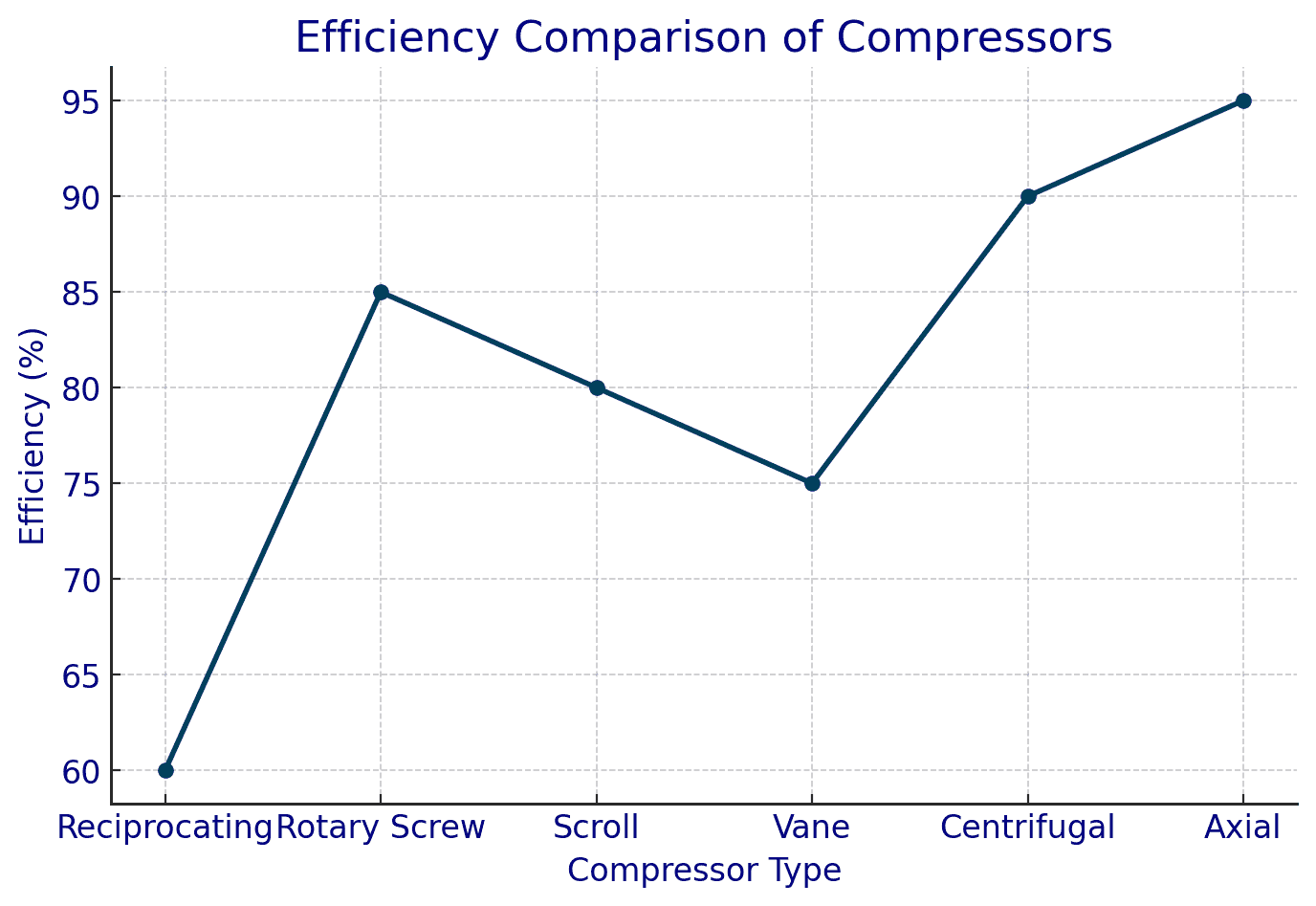
1. Reciprocating Compressors
These compressors use a piston-cylinder mechanism to compress air. They are widely used in automotive workshops, refrigeration, and small-scale industries. Available in single-stage and multi-stage variants, reciprocating compressors provide efficient performance, especially for high-pressure applications.
2. Rotary Screw Compressors
Known for their continuous and smooth operation, these compressors utilize two interlocking helical screws to compress air. They are ideal for industrial use, especially in factories and manufacturing plants, where a steady supply of compressed air is required.
3. Scroll Compressors
These employ two spiral-shaped scrolls to compress air, making them highly efficient and quiet. They are commonly used in HVAC systems, medical equipment, and refrigeration units due to their reliability and low maintenance requirements.
4. Vane Compressors
Utilizing rotating vanes in a cavity, these compressors are known for their efficiency and are often used in applications requiring steady airflow, such as printing, vacuum packaging, and pneumatic tools.
Dynamic Compressors
Dynamic compressors rely on the transfer of kinetic energy to increase gas velocity before converting it into pressure. These include:
1. Centrifugal Compressors
Frequently used in large industrial applications, power plants, and HVAC systems, centrifugal compressors use high-speed impellers to accelerate and compress air. They are preferred for their high efficiency and ability to handle large volumes of air.
2. Axial Compressors
Mostly found in jet engines and gas turbines, these compressors use rotating and stationary blades to compress air efficiently at high speeds. They are crucial in the aerospace and energy production industries.
Choosing the Right Compressor
Choosing the right compressor depends on multiple factors, including pressure requirements, flow rate, energy efficiency, noise levels, maintenance needs, and application type. Understanding these factors helps in selecting the most suitable compressor for a specific industry or operational requirement.
For industrial purposes, rotary screw and centrifugal compressors are often favored due to their continuous operation, durability, and high efficiency. Rotary screw compressors are widely used in manufacturing, construction, and automation due to their ability to provide a steady supply of compressed air with minimal pulsation. They require less maintenance compared to reciprocating compressors and are ideal for applications demanding constant airflow. Centrifugal compressors, on the other hand, are best suited for high-flow, low-pressure applications such as power plants, chemical processing, and HVAC systems, where large volumes of gas or air need to be compressed efficiently.
For smaller-scale applications, reciprocating and scroll compressors provide a cost-effective and reliable solution. Reciprocating compressors, which operate using pistons and cylinders, are widely used in automotive workshops, refrigeration, and home-based applications due to their ability to generate high pressure at lower flow rates. However, they can be noisy and require frequent maintenance due to the movement of mechanical parts. Scroll compressors, which use spiral elements for compression, offer quiet operation, high efficiency, and smooth performance, making them a preferred choice for air conditioning, refrigeration, and medical applications.
When selecting a compressor, it is crucial to consider operational costs, energy consumption, and long-term reliability. A well-chosen compressor can improve productivity, reduce energy costs, and ensure efficient performance in industrial, commercial, and household settings.
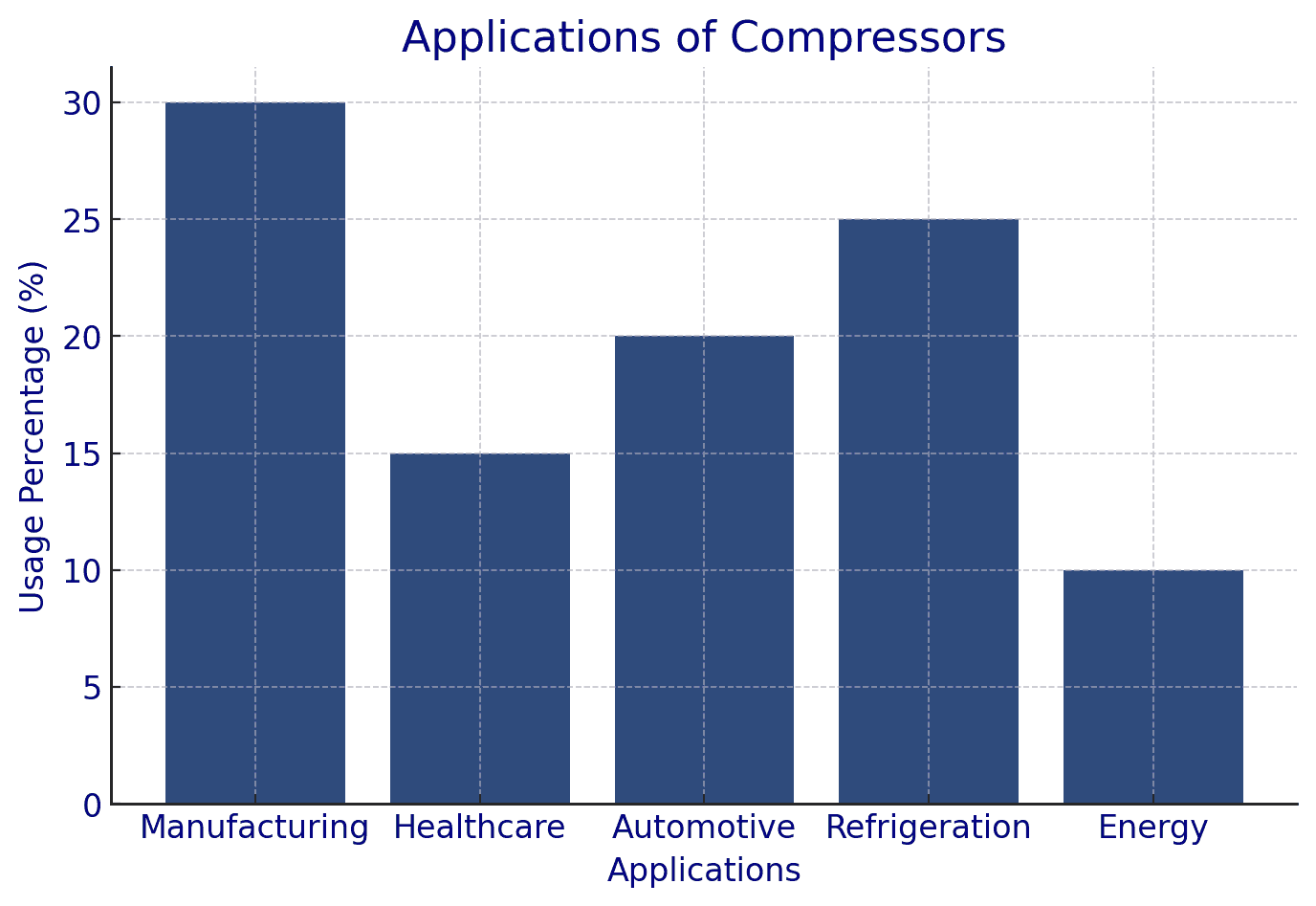
Applications of Compressors
The applications of compressors are vast and diverse:
- Manufacturing: Powering tools and automation systems, enhancing productivity.
- Healthcare: Used in medical ventilators and laboratory equipment.
- Automotive Industry: Used for spray painting, tire inflation, and air brakes.
- Refrigeration & Air Conditioning: Regulating temperature and humidity for comfort.
Innovations in Compressor Technology
With advancements in technology, modern compressors are becoming more energy-efficient and environmentally friendly. Innovations such as:
- Oil-free compressors
- Variable speed drives
- Smart control systems
These developments are reducing energy consumption and minimizing maintenance costs. The future of compressors is geared towards sustainability, with research focusing on reducing carbon footprints and integrating renewable energy sources.
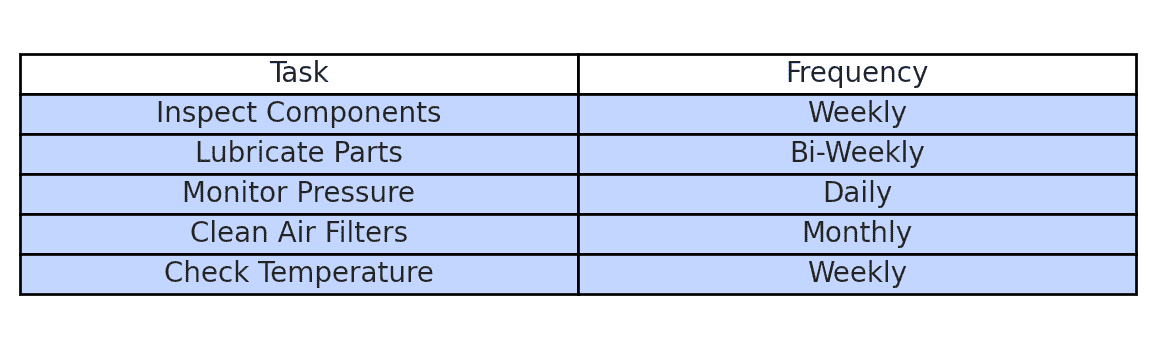
Maintenance of Compressors
Maintaining a compressor is crucial to ensuring its longevity, efficiency, and optimal performance. A well-maintained air compressor not only enhances productivity but also prevents unexpected breakdowns, costly repairs, and energy inefficiencies. Whether used in industrial applications, refrigeration systems, or home workshops, regular maintenance can significantly extend the lifespan of the equipment.
Routine maintenance includes checking and replacing air filters, as clogged filters can reduce efficiency and put excessive strain on the motor. Lubrication of moving parts is essential to minimize wear and tear, especially in reciprocating and rotary screw compressors. Regularly draining moisture from the tank prevents corrosion and contamination, ensuring consistent performance. Inspecting hoses and seals for leaks helps avoid pressure loss, which can affect the compressor’s efficiency.
Additionally, monitoring oil levels, pressure gauges, and temperature readings can help detect potential issues before they lead to significant failures. Keeping the compressor in a clean, well-ventilated area prevents overheating and dust accumulation. Following manufacturer-recommended service schedules ensures smooth operation and extends the unit’s durability.
Regular Inspections and Preventive Maintenance
Conducting routine inspections helps identify potential issues before they escalate. Checking for air leaks, worn-out hoses, and faulty connections ensures the compressor system operates smoothly. Keeping an eye on pressure levels and temperature fluctuations can help detect early warning signs of mechanical failure.
Proper Lubrication for Smooth Operation
Lubrication is a key aspect of compressor maintenance, especially for oil-lubricated compressors. Regularly changing the compressor oil prevents friction, overheating, and premature wear of internal components. Using the right lubricant as recommended by the manufacturer enhances energy efficiency and prolongs the equipment’s lifespan.
Timely Replacement of Worn-Out Parts
Replacing filters, valves, and seals at scheduled intervals prevents air contamination, pressure drops, and reduced performance. A clogged air filter restricts airflow, causing the compressor motor to work harder, leading to increased energy consumption. Timely maintenance of these components ensures consistent air pressure and reliable performance.
Monitoring Pressure Levels and Capacity Limits
Operating a compressor within its designed pressure range prevents overloading and enhances energy savings. Regularly checking the pressure gauge, safety valve, and hoses ensures that the air compressor functions efficiently without risking mechanical stress or overheating.
By following these best practices for compressor maintenance, businesses and homeowners can maximize efficiency, reliability, and cost savings, ensuring uninterrupted operation across various applications.
Conclusion
Compressors are an indispensable part of modern industry and daily life. Their ability to generate and control pressurized air makes them vital in countless applications, from powering heavy machinery to cooling food supplies.
Understanding the various types of compressors and their applications enables businesses and individuals to make informed decisions, optimizing performance and reducing operational costs. As technology continues to evolve, the compressor industry will undoubtedly witness more innovations, making these machines even more efficient and versatile in the years to come.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is the primary function of a compressor?
A compressor increases the pressure of air or gas by reducing its volume, making it useful for various industrial and domestic applications.
2. Which type of compressor is best for continuous operation?
Rotary screw compressors are ideal for continuous operation due to their efficiency and durability.
3. How does a centrifugal compressor work?
A centrifugal compressor uses high-speed impellers to accelerate air and convert its kinetic energy into pressure.
4. What are some common applications of reciprocating compressors?
Reciprocating compressors are widely used in automotive workshops, refrigeration, and small-scale industries for high-pressure applications.
5. How can I extend the lifespan of my compressor?
Regular maintenance, lubrication, pressure monitoring, and operating within the designed capacity can help extend the lifespan of a compressor.
