
Big Data Analysis: Unlocking the Potential of Massive Data Sets
In today’s highly connected world, data is being generated at an unprecedented rate. Imagine unlocking the potential of this vast amount of information. From daily social media activity to data from smart devices and online transactions, an enormous quantity of data is created every second. How can businesses extract meaningful insights from this digital flood? Big Data Analysis has emerged as a powerful tool to make sense of these massive datasets, helping organizations discover valuable patterns that drive better decision-making and refine business strategies. So, how can your organization tap into this data-driven transformation to stay competitive?
What is Big Data?
Big Data refers to datasets that are too large, complex, and fast-moving to be processed using traditional data management tools. These data sets typically exhibit the three Vs:
- Volume: The sheer scale of data being generated continually.
- Velocity: The rapid pace at which data is produced and needs to be processed.
- Variety: The diverse formats and types of data, including structured, semi-structured, and unstructured formats.
Additional concepts such as Veracity (the trustworthiness of the data) and Value (how useful the data is) also play key roles in Big Data’s effectiveness.
Categories of Big Data
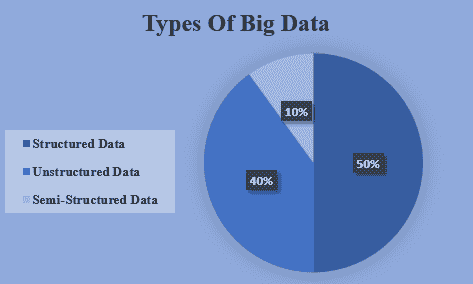
Big Data can be classified into three broad categories:
- Structured Data: This is data that fits neatly into predefined models like tables, making it easy to analyze using conventional methods.
- Unstructured Data: Data that doesn’t conform to a specific model, such as text files, audio, or video content.
- Semi-Structured Data: This type of data may have some organizational structure but doesn't fit perfectly into relational databases, such as XML or JSON files.
Importance of Big Data Analysis
The analysis of Big Data offers organizations the ability to discover patterns, correlations, and trends that would otherwise remain hidden. By processing large volumes of data, businesses can gain powerful insights that drive key decisions and improvements across various sectors. Some of the main benefits of Big Data analysis include:
1. Better Decision-Making
By analyzing vast amounts of data, businesses can make informed decisions, moving beyond guesswork to data-driven strategies.
2. Enhanced Customer Experience
Big Data allows businesses to provide more personalized services, from tailored product recommendations to targeted marketing campaigns, boosting customer satisfaction and loyalty.
3. Increased Operational Efficiency
Identifying inefficiencies and optimizing operations through data analysis can lead to cost savings and higher productivity.
4. Gaining a Competitive Edge
Organizations that harness the power of Big Data can stay ahead of competitors by anticipating market trends, improving products, and refining strategies more quickly.
Tools and Technologies in Big Data Analysis
Effective Big Data analysis relies on specialized tools and technologies capable of processing large datasets. Some of the key technologies include:
Hadoop
Hadoop is an open-source framework that allows data to be stored and processed across distributed systems, enabling organizations to manage large amounts of data at scale.
Apache Spark
Apache Spark is a fast, flexible tool that provides real-time processing capabilities and is compatible with a range of programming languages, making it a popular choice for data processing tasks.
NoSQL Databases
NoSQL databases, such as MongoDB, Cassandra, and HBase, are optimized for handling unstructured and semi-structured data, offering flexibility and scalability beyond traditional relational databases.
Data Visualization Tools
Visualization tools like Tableau, Power BI, and Qlik help present complex data in an intuitive, graphical form, making it easier for decision-makers to understand insights at a glance.
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
AI and machine learning algorithms are increasingly integrated into Big Data workflows, enabling the automation of tasks like predictive analysis and pattern recognition.
Key Phases of Big Data Analysis
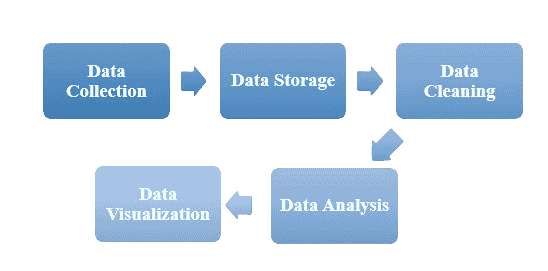
To effectively analyze Big Data and derive valuable insights, the process typically involves several key stages:
1. Data Collection
The first step is gathering data from diverse sources, such as websites, sensors, and social media. Tools like Apache Flume and Kafka are used to facilitate real-time data collection.
2. Data Storage
Once collected, data must be stored efficiently in a secure environment. Distributed storage solutions like Hadoop Distributed File System (HDFS) and cloud platforms are commonly used for Big Data storage.
3. Data Cleaning
Data often requires cleaning to remove duplicates, fill missing values, and correct errors. This step ensures that the dataset is reliable for accurate analysis.
4. Data Analysis
At this stage, analytical methods—such as statistical techniques and machine learning algorithms—are applied to the data to identify meaningful trends and correlations.
5. Data Visualization
The final insights are presented in the form of charts, graphs, and dashboards to make the results accessible and actionable for stakeholders.
Applications of Big Data Analysis
Big Data is being leveraged across numerous sectors to drive innovation and improve operations. Some of the prominent applications include:
Healthcare
In healthcare, Big Data analysis supports better patient care by enabling early disease detection, personalized treatment plans, and more efficient healthcare delivery systems.
E-Commerce
Retailers use Big Data to enhance online shopping experiences by personalizing product recommendations, optimizing pricing strategies, and managing inventory in real time.
Finance
Financial institutions rely on Big Data to detect fraud, evaluate risk, and support algorithmic trading, improving security and operational efficiency.
Transportation
Big Data helps optimize routes, reduce fuel consumption, and streamline logistics, improving transportation systems' overall efficiency.
Education
Educational institutions analyze student performance data to create personalized learning programs and improve teaching methodologies.
Challenges of Big Data Analysis
While Big Data presents enormous opportunities, it also brings several challenges:
Data Privacy and Security
With the increasing volume of sensitive data being processed, protecting privacy and ensuring compliance with regulations, such as GDPR, is a major concern.
Scalability
As the amount of data continues to grow, organizations need scalable systems that can handle the increasing data load efficiently.
Data Quality
Poor-quality data, such as incomplete or inaccurate information, can lead to incorrect conclusions and undermine the value of Big Data analysis.
Skill Shortage
There is a growing demand for skilled professionals in the fields of data science and analytics, creating a talent gap that many organizations struggle to fill.
Emerging Trends in Big Data Analysis
Big Data continues to evolve, with several trends on the horizon that promise to shape its future:
Edge Computing
Edge computing allows for processing data closer to where it is generated, reducing latency and enabling faster real-time analysis.
Blockchain Technology
Blockchain's ability to ensure secure, immutable transactions is being explored to provide greater trust in Big Data applications.
Internet of Things (IoT)
With the increasing number of connected devices, IoT generates constant streams of data. Combining IoT with Big Data analysis enables new insights, such as predictive maintenance and smarter urban infrastructure.
Advanced AI and Machine Learning
As AI and machine learning technologies continue to advance, they will enable even more powerful and automated data analysis capabilities, unlocking new opportunities for Big Data applications.
Conclusion
Big Data Analysis is transforming the way organizations gather insights and make decisions. By leveraging the right tools and technologies, businesses can unlock the true value of their data, driving growth, innovation, and improved performance. As we move further into the digital age, the organizations that harness Big Data’s power will be the ones that thrive in a competitive, data-driven world.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the defining characteristics of Big Data?
- Volume: The vast amount of data generated continuously.
- Velocity: The rapid rate at which data is produced and processed.
- Variety: The diverse formats of data, including structured, semi-structured, and unstructured.
- Additional characteristics include Veracity (data reliability) and Value (usefulness of data).
What are the three categories of Big Data?
- Structured Data: Organized data like tables in relational databases.
- Unstructured Data: Data with no predefined model, e.g., videos, text files.
- Semi-Structured Data: Data with some organizational structure, e.g., JSON or XML files.
What are the benefits of Big Data Analysis?
- Better Decision-Making: Enables data-driven strategies.
- Enhanced Customer Experience: Personalizes services and marketing.
- Increased Operational Efficiency: Identifies inefficiencies and optimizes operations.
- Competitive Edge: Helps predict trends and refine strategies.
Which tools and technologies are commonly used in Big Data Analysis?
- Hadoop: Open-source framework for distributed storage and processing.
- Apache Spark: Real-time processing and flexible analysis tool.
- NoSQL Databases: e.g., MongoDB, Cassandra for unstructured/semi-structured data.
- Data Visualization Tools: Tableau, Power BI for intuitive graphical representation.
- AI and Machine Learning: Automates predictive analysis and pattern recognition.
What are the main phases of Big Data Analysis?
- Data Collection: Gathering data from sources using tools like Apache Flume.
- Data Storage: Using distributed systems like HDFS or cloud platforms.
- Data Cleaning: Ensuring data accuracy by removing errors or duplicates.
- Data Analysis: Applying statistical and machine learning techniques.
- Data Visualization: Presenting results via charts, graphs, and dashboards.
What are some common applications of Big Data?
- Healthcare: Early disease detection and personalized treatment.
- E-Commerce: Personalized recommendations and real-time inventory management.
- Finance: Fraud detection and risk evaluation.
- Transportation: Route optimization and predictive maintenance.
- Education: Analyzing student performance for tailored learning.
What challenges are associated with Big Data Analysis?
- Data Privacy and Security: Ensuring compliance with regulations like GDPR.
- Scalability: Handling the increasing volume of data efficiently.
- Data Quality: Removing inaccuracies to avoid unreliable insights.
- Skill Shortage: Addressing the lack of skilled professionals in data analytics.
What emerging trends are shaping the future of Big Data Analysis?
- Edge Computing: Real-time data processing closer to the source.
- Blockchain: Secure and immutable transaction management.
- IoT Integration: Predictive maintenance and smarter urban planning.
- Advanced AI and Machine Learning: Automated and deeper analysis.
Why is Big Data Analysis important for organizations?
It helps in discovering patterns, making informed decisions, enhancing customer satisfaction, improving operational efficiency, and gaining a competitive edge.
